HTML: Classes vs IDs
To apply certain CSS styles to multiple elements, such as rows representing students in a table, you can use classes. Here’s an example of how you can use classes to style the table rows:
HTML:
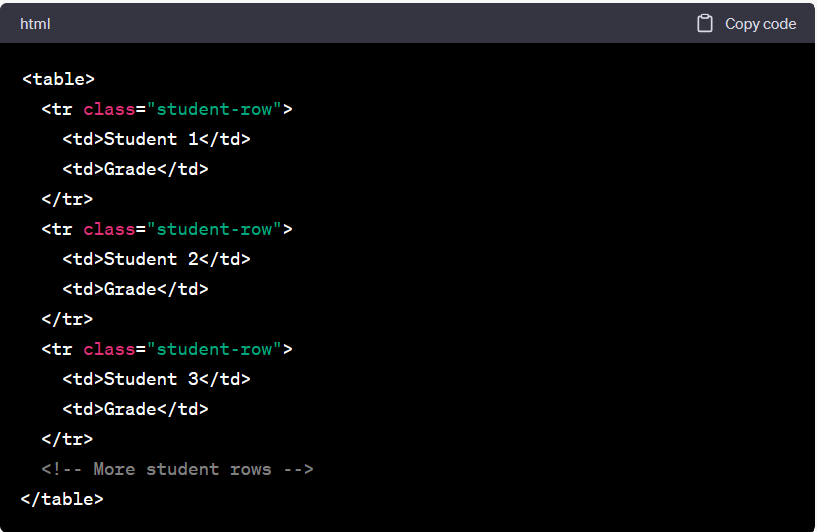
Then, to apply the CSS, we write the following in our CSS file, using the . as the CSS selector for classes:
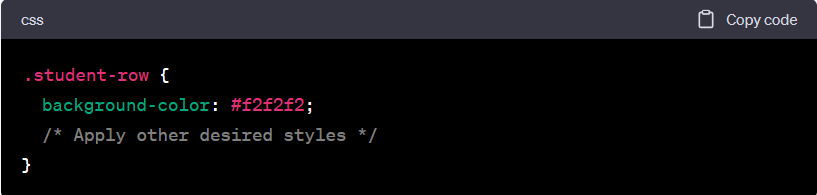
In the above example, the student-row class is added to each <tr> element representing a student in the table. The CSS selector .student-row targets all elements with the student-row class, allowing you to apply specific styles to those rows. In this case, the background color is set to #f2f2f2, but you can add any other desired styles to this class.
By using classes, you can easily target and style multiple elements with a single selector, making your CSS more efficient and maintainable.
IDs
Correct, IDs are unique and can be applied to at most one element on a page. They are typically used to identify a specific element for targeted styling or JavaScript interactions. Let’s continue with the example of the table:
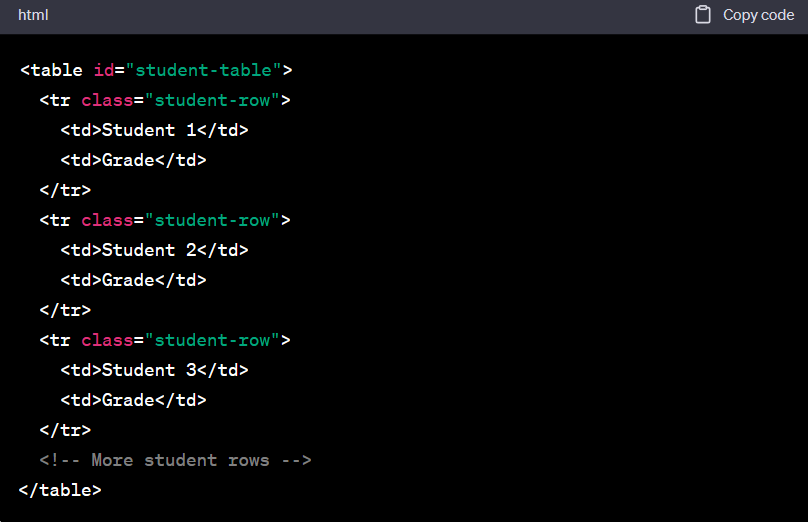
CSS
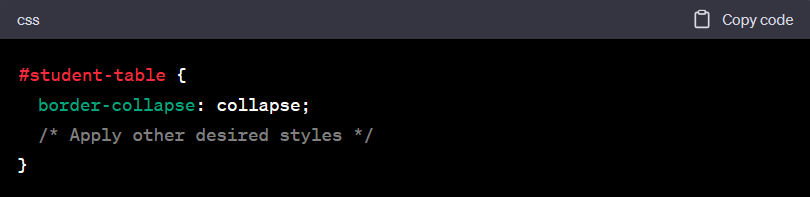
In the example above, we have assigned the ID “student-table” to the <table> element. The CSS selector #student-table targets the element with the specified ID, allowing you to apply specific styles to that table. Here, we’ve applied the border-collapse property to collapse the borders between table cells, but you can add any other desired styles.
Remember that IDs should be unique on a page, while classes can be used on multiple elements. IDs are typically used when you want to target and style a specific element or when you need to reference that element in JavaScript.

Post a comment